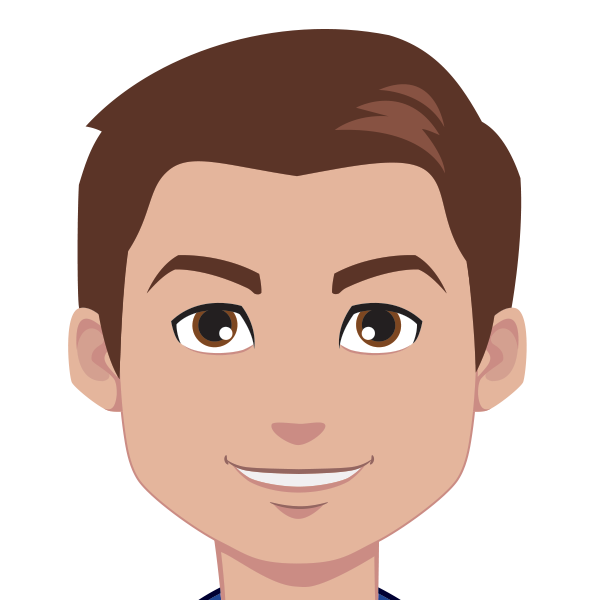
| Atoms, the smallest particles of matter that retain the properties of the matter, are made of protons, electrons, and neutrons. |
原子は、物質の特性を保持する物質の最小粒子であり、陽子、電子、および中性子で構成されています。 |
| Protons have a positive charge, Electrons have a negative charge that cancels the proton's positive charge. |
陽子は正電荷を持ち、電子は陽子の正電荷を打ち消す負電荷を持っています。 |
| Neutrons are particles that are similar to a proton but have a neutral charge. |
中性子は、陽子に似ているが中性の電荷を持つ粒子です。 |
| There are no differences between positive and negative charges except that particles with the same charge repel each other and particles with opposite charges attract each other. |
同じ電荷を持つ粒子は互いに反発し、反対の電荷を持つ粒子は互いに引き合うことを除いて、正電荷と負電荷の間に違いはありません。 |
| If a solitary positive proton and negative electron are placed near each other they will come together to form a hydrogen atom. |
孤立した正の陽子と負の電子が互いに近くに配置されている場合、それらは一緒になって水素原子を形成します。 |
| This repulsion and attraction (force between stationary charged particles) is known as the Electrostatic Force and extends theoretically to infinity, but is diluted as the distance between particles increases. |
この斥力と引力 (静止している荷電粒子間の力) は静電力として知られており、理論的には無限に広がりますが、粒子間の距離が増加するにつれて希釈されます。 |
| When an atom has one or more missing electrons it is left with a positive charge, and when an atom has at least one extra electron it has a negative charge. |
原子に 1 つまたは複数の欠けている電子がある場合、原子には正電荷が残り、原子に少なくとも 1 つの余分な電子がある場合、負電荷があります。 |
| Having a positive or a negative charge makes an atom an ion. |
正または負の電荷を持つと、原子はイオンになります |
| Atoms only gain and lose protons and neutrons through fusion, fission, and radioactive decay. |
原子は、核融合、核分裂、放射性崩壊によって陽子と中性子を獲得したり失ったりするだけです。 |
| Although atoms are made of many particles and objects are made of many atoms, they behave similarly to charged particles in terms of how they repel and attract. |
原子は多くの粒子でできており、物体は多くの原子でできていますが、反発や引き付け方は荷電粒子と同じように振る舞います。 |
| In an atom the protons and neutrons combine to form a tightly bound nucleus. |
原子では、陽子と中性子が結合して、強く結合した原子核を形成します。 |
| This nucleus is surrounded by a vast cloud of electrons circling it at a distance but held near the protons by electromagnetic attraction (the electrostatic force discussed earlier). |
この原子核は、距離を置いて周回する巨大な電子雲に囲まれていますが、電磁引力 (前述の静電力) によって陽子の近くに保持されています。 |
| The cloud exists as a series of overlapping shells / bands in which the inner valence bands are filled with electrons and are tightly bound to the atom. |
雲は、内側の価電子帯が電子で満たされ、原子にしっかりと結合している一連の重なり合うシェル/バンドとして存在します。 |
| The outer conduction bands contain no electrons except those that have accelerated to the conduction bands by gaining energy. |
外側の伝導帯には、エネルギーを得て伝導帯に加速されたものを除いて、電子は含まれていません。 |
| With enough energy an electron will escape an atom (compare with the escape velocity of a space rocket). |
十分なエネルギーがあれば、電子は原子から脱出します (宇宙ロケットの脱出速度と比較してください)。 |
| When an electron in the conduction band decelerates and falls to another conduction band or the valence band a photon is emitted. |
伝導帯の電子が減速して別の伝導帯または価電子帯に落ちると、光子が放出されます。 |
| This is known as the photoelectric effect. |
これは光電効果として知られています |